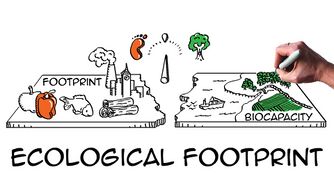
Ecological footprint
It is the impact of human consumption demand. It is the relation between the natural resources that we have and the natural resources that we use.
Humans consume natural resources in excess. They generate waste and produce a negative impact on the environment.
Each city, state or nation´s biocapacity represents the productivity of its natural capital[1]. These areas can also serve to absorb the waste we generate, especially our carbon emissions from burning fossil fuels[2].
Each city, state or nation´s ecological footprint can be compared to its biocapacity, or that of the world.
If a population´s ecological footprint exceeds the region´s biocapacity, that region runs a biocapacity deficit. Its demand for the goods and services that its land and seas can provide- fruit, vegetables, meat, cotton, among others- exceeds what the region´s ecosystems can generate.
The countries with the largest ecological footprints are the USA and China because people consume a lot of natural resources. They consume food, energy, paper, plastic, transport, television, among others. As a consequence, they generate too much waste. They do not reduce, reuse or recycle enough.
National footprint and Biocapacity Accounts
There is an organization called FoDaFo- Footprint Data Foundation- York university, Toronto, Global Footprint Network work together on research and studies. The orgaization´s main purpose is to inform people and to provide the reliability.